Bardet-Biedl syndrome
Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) is a rare autosomal recessive ciliopathy with a highly variable phenotype that evolves significantly during childhood and/or adolescence.28,29 It’s estimated that as many as 2500 people in the United States are living with BBS.25 Obesity and hyperphagia are two common features of BBS that can seriously impact the overall health and quality of life of these patients.28,29
“It’s a constant need to eat. And that’s when she started sneaking foods... We ended up getting some locks and putting them on our pantry and on the fridge.”
Olivia, whose daughter Adalissa is living with BBS
Common features
Obesity (72%-92%)46
- Typically early onset by age 5
Hyperphagia (insatiable hunger)4
- Preoccupation with food
- Excessive food-seeking behavior
Visual impairment (93%)29
Rod-cone dystrophy that presents as atypical retinitis pigmentosa with early macular involvement
- Symptoms generally appear in the first decade of life and ultimately lead to legal blindness by teens/early adulthood
- Progressive visual loss manifests initially as night blindness, followed by photophobia, and finally a loss of central/color vision
- Changes in the retina can be detected by electroretinography (ERG) by age 2
- Significant changes are typically not evident until after age 5
Renal anomalies (53%)
- Renal phenotype is variable. Generally involves cystic tubular disease and anatomical malformations29
Cognitive impairment (>50%)28
- Learning difficulties
- Speech delay
- Developmental delay
Other features29,51
- Genital anomalies
- Diabetes mellitus
- Dental anomalies
- Left ventricular hypertrophy or congenital heart disease
- Brachydactyly or syndactyly
- Mild spasticity (especially lower limbs)
- Strabismus, cataracts, or astigmatism
- Ataxia or poor coordination
- Anosmia or hyposmia
- Polyuria or polydipsia
- Hepatic fibrosis
BBS has a highly variable phenotype that evolves significantly during childhood and/or adolescence.
Phenotype can vary between siblings.
Pathology
Obesity and hyperphagia in BBS:
Likely driven by impairment of a key signaling pathway that regulates hunger57
The MC4R pathway1,57
- Plays a key role in regulating hunger, satiety, and energy expenditure
- Is activated by leptin, a neurosignaling hormone generated in adipose tissue
Take a deeper look inside the MC4R pathway
Hyperphagia in BBS
Hyperphagia is a key symptom associated with obesity in BBS and often has an early onset, typically by age 5.4
General dimensions of hyperphagia23
Behavior
Excessive food-seeking behavior
Drive
Preoccupation with food
Severity
Significant distress when denied food
Patients with BBS suffer from hyperphagia, exhibiting extreme food-seeking behavior.4
Total hyperphagia score and subscale scores in 13 patients with BBS*
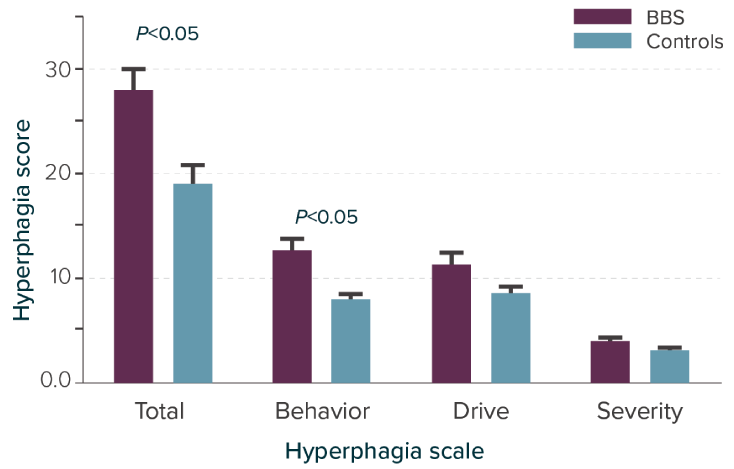
Adapted from Sherafat-Kazemzadeh R et al. Pediatr Obes. 2013;8(5):e64-e67.
Hyperphagia and food-seeking behavior are different in BBS
Individuals living with BBS have significantly greater hyperphagia scores overall (total) and in the behavioral dimension compared to matched controls.
*A hyperphagia questionnaire assessing 13 patients with BBS and 23 nonsyndromic controls with similar age, sex, and BMI z-score. After adjustment for age, sex, race, and BMI z-score, total score (P=0.032) and behavior subscale (P=0.003) remained significantly different.
Consider the Understanding the Impact of Hyperphagia tool for discussions with individuals living with BBS and their families.
Obesity in BBS
As many as 9 out of 10 patients with BBS are affected by obesity.29
BMI z-scores by gender and age group in children with BBS (n=628)46
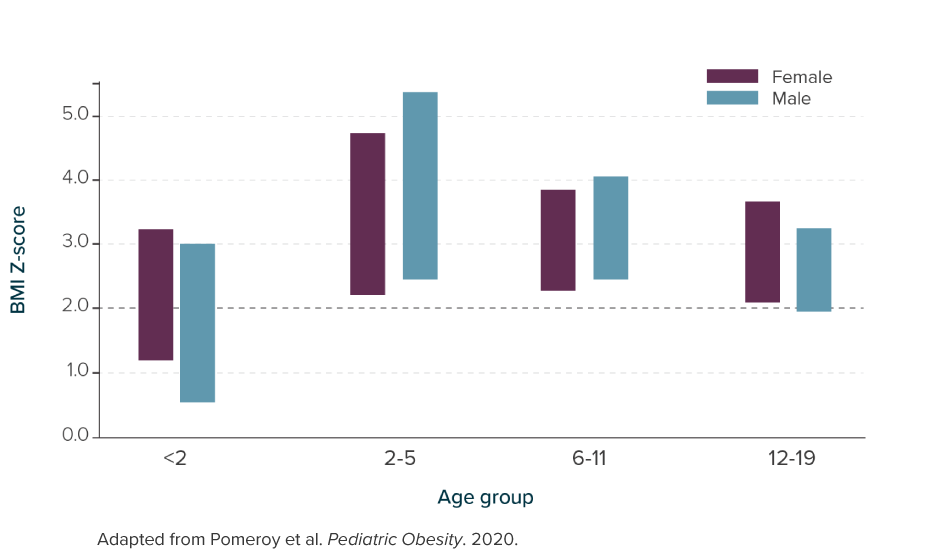
Severe obesity has an early onset, typically beginning in childhood by age 5, and persists into adulthood46
Obesity further complicates management of comorbidities.
Diabetes
Renal
impairment
Hypertension
Chronic obesity and hyperphagia management are challenging in patients with BBS.
Diet and behavioral modifications
Diet and exercise are not always enough when living with a rare genetic disease of obesity like BBS
Pharmacotherapies
Not all treatments target the MC4R pathway, a root cause of obesity and hunger in people living with BBS57
Bariatric surgery
May be complicated due to associated comorbidities
Listen to Dr. Robert Haws discuss hyperphagia and obesity in BBS
Resources
Videos
Pathway deficiencies in BBS
Searching for answers
The Role of the MC4R Pathway
Downloads
MC4R=melanocortin-4 receptor; POMC=proopiomelanocortin.
-
References
-
Huvenne H, Duberne B, Clément K, Poitou C. Rare genetic forms of obesity: clinical approach and current treatments in 2016. Obes Facts. 2016;9(3):158-173.
-
Ellacott KL, Cone RD. The role of the central melanocortin system in the regulation of food intake and energy homeostasis: lessons from mouse models. Philos Trans R Soc Land B Biol Sci. 2006;361(1471):1265-1274.
-
Hales CM, Fryar CD, Carroll MD, Freedman DS, Ogden CL. Trends in obesity and severe obesity prevalence in US youth and adults by sex and age,
2007-2008 to 2015-2016. JAMA. 2018;319(16):1723-1725. -
Sherafat-Kazemzadeh R, Ivey L, Kahn SR, et al. Hyperphagia among patients with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Pediatr Obes. 2013;8(5):e64-e67.
-
Ward ZJ, Long MW, Resch SC, Giles CM, Cradock AL, Gortmaker SL. Simulation of growth trajectories of childhood obesity into adulthood. N Engl J Med.
2017;377(22):2145-2153. -
Data on file. Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Boston, MA.
-
Styne DM, Arslanian SA, Connor EL, et al. Pediatric obesity-assessment, treatment, and prevention: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(3);709-757. -
Cuda S, Censani M, O’Hara V, et al. Pediatric Obesity Algorithm eBook. Obesity Medicine Association. 2020-2022.
http://www.obesitymedicine.org/childhood-obesity. Accessed June 8, 2021. -
Morton GJ, Meek TH, Schwartz MW. Neurobiology of food intake in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014;15(6):367-378.
-
van der Klaauw AA, Farooqi IS. The hunger genes: pathways to obesity. Cell. 2015;161(1):119-132.
-
da Fonseca ACP, Mastronardi C, Johar A, Arcos-Burgos M, Paz-Filho G. Genetics of non-syndromic childhood obesity and the use of high-throughput DNA sequencing technologies. J Diabetes Complications. 2017;31(10):1549-1561.
-
Yazdi FT, Clee SM, Meyre D. Obesity genetics in mouse and human: back and forth, and back again. PeerJ. 2015;3:e856.
-
Burns B, Schmidt K, Williams SR, Kim S, Girirajan S, Elsea SH. Rai1 haploinsufficiency causes reduced Bdnf expression resulting in hyperphagia, obesity and altered fat distribution in mice and humans with no evidence of metabolic syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19(20):4026-4042.
-
Lu Q, Yang Y, Jia S, et al. SRC1 deficiency in hypothalamic arcuate nucleus increases appetite and body weight. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018:JME-18-0075.R2.
-
Vaisse C, Reiter JF, Berbari NF. Cilia and obesity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017;9(7):a028217.
-
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405-424.
-
Sequencing Sample Reports: Indeterminate (with CNV). Prevention Genetics. Updated October 18, 2009. https://www.preventiongenetics.com/ClinicalTesting/TestCategory/sampleReports. Accessed November 11, 2021.
-
A guide to understanding variant classification. Blueprint Genetics. https://blueprintgenetics.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Variant_Classification_WP_VARA41-06-FINAL.pdf. Accessed November 11, 2021
-
VUS – the most maligned result in genetic testing. Blueprint Genetics. Updated October 29, 2020. https://blueprintgenetics.com/resources/vus-the-most-maligned-result-in-genetic-testing/. Accessed November 11, 2021.
-
Bean LJH, Tinker SW, da Silva C, Hegde MR. Free the data: one laboratory’s approach to knowledge-based genomic variants classification and preparation for EMR integration of genomic data. Hum Mutat. 2013;34:1183-1188.
-
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Entries 609734, 600955, and 614963. https://www.omim.org/. Accessed November 18, 2021.
-
Kohlsdorf K, Nunziata A, Funcke JB, et al. Early childhood BMI trajectories in monogenic obesity due to leptin, leptin receptor, and melanocortin 4 receptor deficiency. Int J Obes (Lond). 2018;42(9):1602-1609.
-
Heymsfield SB, Avena NM, Baier L, et al. Hyperphagia: current concepts and future directions proceedings of the 2nd international conference on hyperphagia. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014;22 Suppl 1(0 1):S1-S17.
-
Shah BP, Moeller IH, Van der Ploeg LHT, Garfield AS. Identification and functional characterization of novel variants in genes in the MC4R pathway associated with severe early-onset obesity and hyperphagia. Oral presentation at: Keystone Symposia. February 2019. Banff, Alberta, Canada.
-
Rhythm 10-K Annual Report (2020). Rhythm Pharmaceuticals. Accessed November 11, 2021.
-
Rhythm 10-K Annual Report (2024). Rhythm Pharmaceuticals. Accessed March 15, 2024.
-
Ayers KL, Glicksberg BS, Garfield AS, et al. Melanocortin 4 Receptor pathway dysfunction in obesity: patient stratification aimed at MC4R agonist treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103:2601-2612.
-
Forsythe E, Kenny J, Bacchelli C, Beales PL. Managing Bardet-Biedl syndrome—now and in the future. Front Pediatr. 2018;6:23.
-
Forsythe E, Beales PL. Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013;21(1):8-13.
-
Pigeyre M, Yazdi FT, Kaur Y, Meyre D. Recent progress in genetics, epigenetics and metagenomics unveils the pathophysiology of human obesity. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016;130(12):943-986.
-
Joy T, Cao H, Black G, et al. Alström syndrome (OMIM 203800): a case report and literature review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:49.
-
Van Groenendael S, Giacovazzi L, Davison F, et al. High quality, patient centred and coordinated care for Alstrom syndrome: a model of care for an ultra-rare disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015;10:149.
-
Waters AM, Beales PL. Ciliopathies: an expanding disease spectrum. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011;26:1039.
-
Paisey RB, Steeds R, Barrett T, et al. Alström Syndrome. GeneReviews®. February 7, 2003. Updated June 13, 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1267/. Accessed November 10, 2021.
-
Coll AP, Farooqi SI, Challis BG, Yeo GSH, O’Rahilly S. Proopiomelanocortin and energy balance: insights from human and murine genetics. J Clin Endocrinal Metab. 2004,89:2557.
-
Mendiratta MS, Yang Y, Balazs AE, et al. Early onset obesity and adrenal insufficiency associated with a homozygous POMC mutation. Int J Pediatr Endocrinal. 2011;5.
-
National Institutes of Health. POMC deficiency. MedlinePlus®. Updated August 18, 2020. https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/proopiomelanocortin-deficiency/. Accessed November 10, 2021.
-
Farooqi IS, Wangensteen T, Collins S, et al. Clinical and molecular genetic spectrum of congenital deficiency of the leptin receptor. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:237.
-
Stijnen P, Ramos-Molina B, O’Rahilly S, et al. PCSK1 mutations and human endocrinopathies: from obesity to gastrointestinal disorder. Endocr Rev. 2016;37(4):347-371.
-
Martin MG, Lindberg I, Solorzano-Vargas RS, et al. Congenital proprotein convertase 1/3 deficiency causes malabsorptive diarrhea and other endocrinopathies in a pediatric cohort. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(1):138-148.
-
Rui L. SH2B1 regulation of energy balance, body weight, and glucose metabolism. World J Diabetes. 2014;5:511.
-
Doche ME, Bochukova EG, Su HW, et al. Human SH2B1 mutations are associated with maladaptive behaviors and obesity. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:4732.
-
Yang Y, van der Klaauw AA, Zhu L, et al. Steroid receptor coactivator-1 modulates the function of Pomc neurons and energy homeostasis. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1718.
-
Cacciottolo TM, Perikari A, van der Klaauw A, et al. Rare variants in Steroid Receptor Coactivator-1 (SRC-1) associated with obesity, adipose tissue dysfunction and liver fibrosis. QJM. 2019;112(9);724-729.
-
National Institutes of Health. Bardet-Biedl syndrome. MedlinePlus®. Updated August 18, 2020. https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/bardet-biedl-syndrome/#inheritance. Accessed June 15, 2021.
-
Pomeroy J, Krentz AD, Richardson JG, et al. Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Pediatr Obes. 2021;16:e12703.
-
Forsythe E, Sparks K, Hoskins BE, et al. Genetic predictors of cardiovascular morbidity in Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Clin Genet. 2015;87(4):343-349.
-
Vos N, Oussaada S, Cooiman MI, et al. Bariatric surgery for monogenic non-syndromic and syndromic obesity disorder. Curr Diab Rep. 2020;20(44):1-10.
-
Kenny J, Forsythe E, Beales P, Bacchelli C. Toward personalized medicine in Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Per Med. 2017;14(5):447-456.
-
Poitou C, Mosbah H, Clement K. Mechanisms in endocrinology: update on treatments for patients with genetic obesity. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020;183(5):R149-R166.
-
Srivastava G, Apovian CM. Current pharmacotherapy for obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(1):12-24.
-
Beales PL, Elcioglu N, Woolf AS, Parker D, Flinter FA. New criteria for improved diagnosis of Bardet-Biedl syndrome: results of a population survey. J Med Genet. 1999;36(6):437-446.
-
Forsyth R, Gunay-Aygun M. Bardet-Biedl syndrome overview. GeneReviews®. July 14, 2003. Updated July 23, 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1363/. Accessed November 10, 2021.
-
Alvarez-Satta M, Castro-Sanchez C, Valverde D. Alström syndrome: current perspectives. Appl Clin Genet. 2015;8:171-179.
-
Nordang GBN, Busk OL, Tveten K, et al. Next-generation sequencing of the monogenic obesity genes LEP, LEPR, MC4R, PCSK1 and POMC in a Norwegian cohort of patients with morbid obesity and normal weight controls. Mol Genet Metab. 2017;121:51.
-
Aliferis K, Helle S, Gyapay G, et al. Differentiating Alström from Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) using systemic ciliopathy genes sequencing. Ophthalmic Genet. 2012;33(1): 18-22.
-
Eneli I, Xu J, Webster M, et al. Tracing the effect of the melanocortin-4 receptor pathway in obesity: study design and methodology of the TEMPO registry. Appl Clin Genet. 2019;12:87-93.
-
Seo S, Guo DF, Bugge K, Morgan DA, Rahmouni K, Sheffield VC. Requirement of Bardet-Biedl syndrome proteins for leptin receptor signaling. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18(7):1323-1331.
-
Courbage S, Poitou S, Le Beyec – Le Bihan J, et al. Implication of heterozygous variants in genes of the leptin-melanocortin pathway in severe obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;106(10):2991-3006.
-